 |
In this research, a differential wheel velocity type mobile robot is used for the human-following robot. Since the DINDs take charge of the sensing and processing in ISpace, the mobile robots do not need any special functions nor devices, except for an ability to move and a wireless network device to allow for communication with the DINDs. Moreover, since this type of robot has a simple and compact structure, it is suitable for a physical agent that has to interact with humans in complicated environments. Our mobile robot is based on the Pioneer2-DX by ActivMedia Robotics[13].
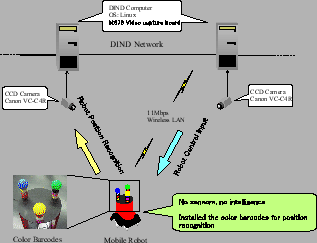
This mobile robot is connected to the DIND network via wireless LAN, as shown in Fig.3, and shares the resources of the DINDs. For estimating the position of the robot, three color barcodes are installed around the mobile robot. The pattern of the color barcode is recognized by the DIND and it estimates the posture and position of the robot. Since the height of the mobile robot is already known, the position of a mobile robot is reconstructed from one camera image. Details are written in [14]. Three color bar codes are installed so that these construct an equilateral triangle on the top of the mobile robot. Since the center of this equilateral triangle is calculated from the positions of these color barcodes, the position and posture of a mobile robot are achieved. Although all of the three color barcodes cannot be always recognized, it is possible to calculate the position and posture of the robot when at least two of them are detected.